Cold Sores, Genital Herpes, and More: Unmasking the Secrets of HSV Infections
I. Introduction
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) is a pervasive viral infection that affects millions of people worldwide. While it may not always be in the spotlight, understanding HSV is of paramount importance.
In this article, we’ll delve into the world of HSV, exploring its types, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies. HSV’s impact on individuals’ lives goes far beyond physical symptoms, encompassing emotional and psychological aspects as well.
II. Background Information
HSV, short for Herpes Simplex Virus, belongs to a family of viruses known for causing various infections in humans. It is classified into two primary types: HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 is often associated with oral herpes, manifesting as cold sores or fever blisters around the mouth.
In contrast, HSV-2 is linked to genital herpes, characterized by painful sores in the genital and anal areas. However, it’s essential to recognize that both HSV-1 and HSV-2 can infect either location, blurring the boundaries between oral and genital herpes.
As for transmission, HSV is a highly contagious virus. It can spread through direct contact with infected sores or through asymptomatic shedding, where the virus is present on the skin or mucous membranes without visible symptoms.
Sexual contact is a common mode of transmission, but HSV can also be spread through non-sexual means, such as oral-to-oral contact or sharing personal items like towels or razors.
III. Types of HSV
Understanding the differences between HSV-1 and HSV-2 is crucial. HSV-1 typically prefers the oral region, causing cold sores or oral herpes. It can also infect the genital area, leading to genital herpes through oral-genital contact.
Conversely, HSV-2 predominantly infects the genital area but can also affect the mouth. Regardless of their primary location, both types can cause recurrent outbreaks and lead to long-term infections.
IV. Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of HSV infection can vary widely from person to person. Some individuals may experience severe outbreaks with painful, blistering sores, while others may remain asymptomatic, showing no visible signs of infection.
Common symptoms include itching, burning, tingling sensations, and flu-like symptoms during initial outbreaks. It’s important to note that even when symptoms are absent, the virus can still be contagious, making it challenging to prevent transmission.
V. Diagnosis and Testing
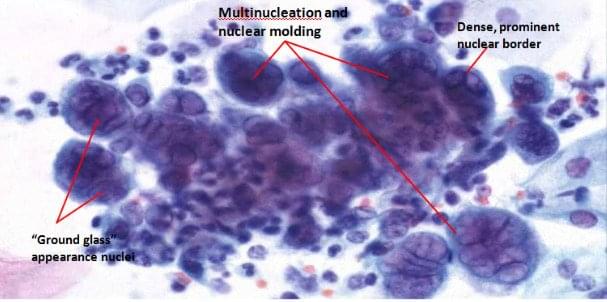
Diagnosing HSV often requires a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Healthcare professionals may examine visible sores and inquire about symptoms.
Laboratory tests such as viral culture, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and blood tests can confirm the presence of the virus and distinguish between HSV-1 and HSV-2. Seeking medical consultation is vital for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
VI. Treatment Options
The management of HSV primarily revolves around antiviral medications, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir. These medications can reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks, helping individuals lead healthier lives.
Additionally, lifestyle modifications like stress management, maintaining a strong immune system, and practicing good hygiene can contribute to symptom relief.
Early treatment is essential in managing HSV effectively. Antiviral medications work best when started during the early stages of an outbreak or taken regularly to suppress the virus.
By seeking medical advice and promptly initiating treatment, individuals can minimize the impact of HSV on their lives.
VII. Complications and Long-Term Effects
Untreated or poorly managed HSV infections can lead to several complications. One of the most significant concerns is the potential for transmitting the virus to sexual partners, especially during outbreaks. Additionally, HSV infection has been linked to an increased susceptibility to other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including HIV.
Thus, managing HSV is not only essential for one’s health but also for preventing the spread of other infections.
VIII. Preventive Measures
Preventing HSV transmission involves a combination of strategies. Safe sexual practices, such as using condoms and dental dams, can reduce the risk of infection during sexual contact. Avoiding sexual activity during active outbreaks is crucial to preventing transmission.
Open communication with sexual partners about HSV status and taking precautions can significantly reduce the risk of spreading the virus.
IX. Living with HSV
Living with an HSV diagnosis can be emotionally challenging due to the stigma associated with the virus. However, it’s important to know that HSV is a manageable condition. Building strong relationships, seeking support from healthcare professionals and support groups, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are key aspects of managing HSV effectively.
Reducing stigma and promoting awareness can also contribute to a more empathetic and informed society.
X. Research and Future Developments
Ongoing research efforts are dedicated to developing effective vaccines and exploring new treatment approaches for HSV. While no vaccine is currently available, progress is being made, offering hope for better prevention and management options in the future.
Staying informed about these developments is essential for individuals living with HSV and those seeking to prevent infection.
XI. Conclusion
In conclusion, Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) is a prevalent viral infection that affects many people. Understanding its types, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies is crucial for individuals and society as a whole.
By recognizing the importance of early diagnosis, seeking medical advice, and practicing safe behaviors, we can reduce the impact of HSV and promote healthier lives. Additionally, reducing the stigma associated with HSV is essential for supporting those affected by the virus.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):
- The CDC website provides comprehensive information on HSV, including statistics, transmission, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. You can find up-to-date information and statistics related to HSV on their website.
- World Health Organization (WHO):
- WHO also offers valuable information on HSV, its global prevalence, and guidelines for prevention and management. Their website is a reputable source for international data and recommendations.
- Medical Journals:
- Look for articles and studies published in respected medical journals like JAMA, The New England Journal of Medicine, and the Journal of Infectious Diseases. These journals often contain peer-reviewed research on HSV and related topics.
- Academic Databases:
- Databases like PubMed, Google Scholar, and ResearchGate can help you find scientific studies, clinical trials, and scholarly articles related to HSV. You can search for specific topics, treatments, or epidemiological data.
- Government Health Departments:
- State or regional health departments often provide localized information and statistics on HSV. Check your local health department’s website for relevant data and resources.
- Herpes Support Organizations:
- Organizations like the American Sexual Health Association (ASHA) or the International Herpes Alliance may offer valuable resources, articles, and statistics related to HSV.
- Books and Textbooks:
- Books on virology, infectious diseases, or sexual health may contain chapters dedicated to HSV. Look for textbooks written by experts in the field.
- Clinical Guidelines:
- Clinical guidelines published by professional medical associations can provide insights into the recommended diagnostic and treatment approaches for HSV.