Beyond Digestion: Discover How Probiotics Are Rewriting the Rules in the Fight Against Obesity and Diabetes
In recent years, the scientific community has turned its attention to the human gut microbiota, uncovering its profound influence on overall health and disease.
Among the most intriguing findings is the role of probiotics, live microorganisms that offer health benefits when administered in adequate amounts. These microscopic allies have sparked a revolution in how we approach some of the most challenging health issues of our time, particularly obesity and diabetes.
This extensive exploration delves deep into the science behind probiotics and their potential as a therapeutic agent in these prevalent conditions.
What are Probiotics?
Probiotics are not a singular entity but a diverse group of live microorganisms, primarily bacteria and yeasts, that are beneficial to our health, particularly our digestive system. They are commonly found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut and are also available as dietary supplements.
The primary function of these microbes is to maintain a healthy balance in our gut microbiota, which is essential for optimal digestive health, immune function, and more. Understanding the complex interactions between these microorganisms and our body is key to unraveling their therapeutic potential.
The Link between Probiotics, Obesity, and Diabetes
Obesity and diabetes are two of the most critical public health challenges of the 21st century. They are often interconnected, with obesity being a significant risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes. The gut microbiota plays a pivotal role in this link.
An imbalance in the gut microbiota can lead to a cascade of metabolic disruptions, contributing to the development and progression of both obesity and diabetes. Probiotics can help restore this balance, potentially mitigating the risk factors and effects of these conditions.
Can Probiotics Treat Obesity?
The relationship between gut microbiota and obesity is complex and multifaceted. Obesity has been associated with changes in the composition and function of the gut microbiota.
These changes can influence energy metabolism, fat storage, and inflammatory pathways, which are crucial in the development of obesity.
Probiotics can modulate the gut microbiota, reducing inflammation and altering metabolism in a way that favors weight loss and improved health.
Impact on Liver Fat and Weight Loss
The liver plays a vital role in metabolism and energy storage. In obese individuals, the liver often accumulates excessive fat, leading to NAFLD. Probiotics can influence liver function by reducing fat accumulation, thereby lowering the risk of NAFLD. They also contribute to overall weight loss by positively affecting metabolism and energy expenditure.
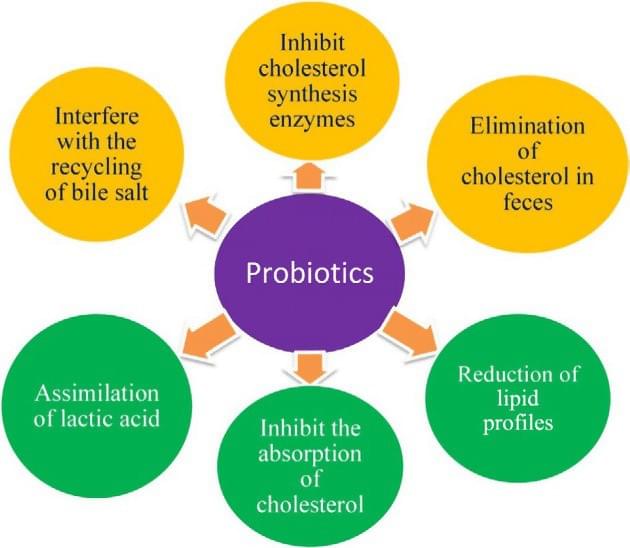
Cholesterol Reduction
High cholesterol is a common comorbidity in obesity, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Probiotics can lower cholesterol levels through various mechanisms, including the breakdown and assimilation of cholesterol by probiotic bacteria. This cholesterol-lowering effect is not only beneficial for weight management but also for cardiovascular health.
Can Probiotics Help Manage Diabetes?
The role of probiotics in diabetes management is an area of growing interest. The gut microbiota influences various aspects of glucose metabolism, which is critically disrupted in diabetes. By modulating the gut microbiota, probiotics can enhance insulin sensitivity, improve glucose control, and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity
Insulin resistance is a hallmark of type 2 diabetes. Probiotics can enhance insulin sensitivity by altering the production of short-chain fatty acids in the gut, which play a role in metabolic regulation. Improved insulin sensitivity means better glucose uptake by cells, reducing blood sugar levels.
Reducing Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a feature of both obesity and diabetes. Probiotics can exert anti-inflammatory effects, potentially reducing the chronic low-grade inflammation associated with these conditions. This anti-inflammatory action is crucial, as it can slow down the progression of diabetes and reduce the risk of its complications.
Should You Start Taking Probiotics?
While the benefits of probiotics are promising, their use should be considered as part of a broader lifestyle approach to health. Probiotics can be found in various natural sources and supplements, and their intake should be balanced with other dietary and lifestyle choices.
It’s essential to choose high-quality probiotic supplements and integrate them into a healthy diet and active lifestyle for optimal benefits.
The Role of Diet and Lifestyle
A holistic approach to managing obesity and diabetes involves more than just probiotics. It encompasses a balanced diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep. While probiotics can contribute significantly to gut health, they are most effective when combined with other healthy lifestyle practices.
Conclusion
The exploration into the world of probiotics and their impact on obesity and diabetes is an ongoing journey. While current evidence points to their beneficial role, more research is needed to fully understand their long-term effects and optimal application.
For now, they offer a natural, complementary approach to managing these complex conditions, holding promise for a future where gut health is central to our overall well-being.
References:
- Moseti et al: Molecular regulation of adipogenesis and potential anti-adipogenic bioactive molecules.
- Christ et al: Western diet and the immune system: an inflammatory connection.
- Das et al: Current status of probiotics and related health benefits.
- Narmaki et al: The combined effects of probiotics and restricted calorie diet on the anthropometric indices, eating behaviour, and hormone levels of obese women with food addiction: a randomized clinical trial.
- Pereira and Gibson: Cholesterol assimilation by lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria isolated from the human gut.
- Tsalamandris et al: The role of inflammation in diabetes: current concepts and future perspectives.